Distribution Pipes
Distribution Pipes are essential components of infrastructure systems used to convey fluids from a central source to multiple endpoints for consumption or use. These networks consist of interconnected pipes that span varying distances, ranging from localized building systems to extensive municipal grids. They are constructed from diverse materials such as metals plastics and composites, chosen based on factors like durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The design of distribution pipe networks considers parameters such as flow rates, pressure requirements, environmental conditions, and future expansion needs.
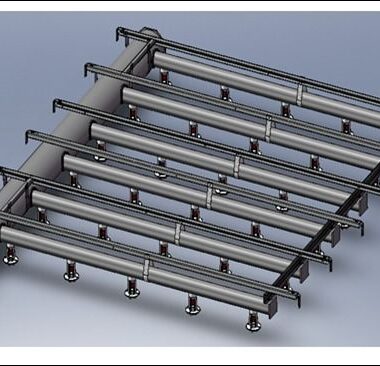
Distribution Pipes
Application and Importance of
- Water Supply: Distributing potable water from treatment plants to homes, businesses, and public facilities.
- Gas Distribution: Transporting natural gas or other gases from production sites to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers.
- Chemical Transport: Conveying chemicals and industrial fluids within manufacturing facilities or from suppliers to end-users.
- Oil Pipelines: Transmitting crude oil and refined products over long distances from production fields to refineries and distribution centers.
- Wastewater Systems: Carrying sewage and wastewater away from homes and businesses to treatment plants for processing and disposal.
- Cooling Systems: Circulating chilled water or other coolants in HVAC systems and industrial cooling applications.
- Fire Protection: Providing water distribution for firefighting purposes through fire hydrants and sprinkler systems.
Distribution Pipes
Advantages of
- Efficient Transport: Facilitates the efficient and reliable transport of fluids over long distances and across various points of use.
- Resource Utilization: Enables centralized management and distribution of resources such as water, gas, or chemicals.
- Versatility: Can be constructed from a variety of materials to suit different applications and environmental conditions.
- Cost-Effective: Provides a cost-effective solution for delivering fluids compared to alternative methods like tankers or individual transport systems.
- Reliability: Offers consistent delivery of fluids, minimizing disruptions and ensuring continuous supply to end-users.
- Infrastructure Support: Supports urban development and industrial operations by providing essential utilities to residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Other Cooling Tower Spares We Manufacture
Honeycomb PVC Fills
Honeycomb PVC Fills are a type of fill media used in cooling towers, made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). They feature a honeycomb-like structure that maximizes the surface area

Drift Eliminators
Drift Eliminators are essential components in cooling towers designed to minimize the loss of water droplets, known as drift, that are carried out of the tower by the exiting airflow.
Axial Fan
Axial Fan is a type of fan that moves air along the axis of its blades. It typically consists of a motor and blades mounted on a shaft within a cylindrical housing. Axial fans are designed

Motors
Motors are specially designed electric motors used to drive fans in cooling towers. They are typically robust and corrosion-resistant, often made of materials like stainless steel

FRP Casing
FRP Casing refers to casings or enclosures made from Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP). FRP is a composite material consisting of a polymer matrix reinforced with fiberglass fibers.

Sprinkler
Sprinkler in cooling towers are mechanical devices designed to evenly distribute water over the fill media inside the tower. They play a crucial role in the cooling process

Nozzles
Nozzles in cooling towers are devices designed to distribute water evenly over the fill material inside the tower. They play a critical role in facilitating efficient heat transfer

Gearbox
Gearbox in a cooling tower is a mechanical component that serves to transmit and control the rotational speed and torque of the fan or other moving parts within the tower.

Structure and Hardware
Structure and Hardware of a cooling tower encompass its physical framework and essential components designed to facilitate heat dissipation.

