Introduction
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is transforming the way cooling towers are designed and optimized. It uses advanced mathematical algorithms to simulate fluid flow, heat transfer, and other critical dynamics inside cooling towers, providing engineers with insights that traditional design methods cannot easily achieve. Cooling towers, integral to various industries such as power generation, HVAC, and chemical processing, rely on efficient heat exchange processes to function effectively. With CFD, these processes are analyzed in much greater detail, allowing for better performance, efficiency, and overall system design.
Benefits of CFD in Cooling Tower Design
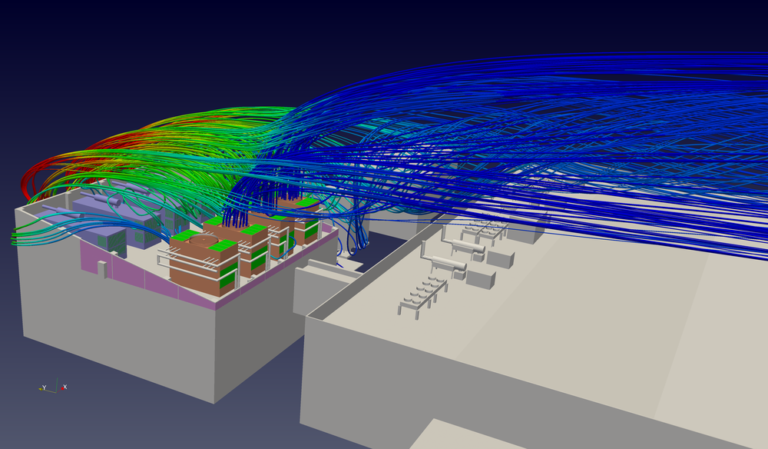
Detailed Fluid Flow Analysis: CFD provides an in-depth look at the airflow patterns and water droplets’ behavior within the cooling tower. This allows engineers to spot inefficiencies in the air and water distribution and correct them before finalizing the design.
Energy Optimization: Cooling towers consume significant amounts of energy, particularly in the operation of fans and pumps. CFD simulations help minimize energy consumption by optimizing airflow and reducing pressure drop within the tower.
Thermal Performance Evaluation: By simulating various thermal conditions, CFD helps predict how the cooling tower will perform under different environmental and operational scenarios. This ensures the design meets the required cooling load while considering real-world conditions such as humidity, temperature, and wind.
Structural Integrity Testing: CFD models can assess the cooling tower’s structural integrity under extreme conditions such as high wind loads, seismic activity, or large temperature differentials. This enhances the safety and durability of the design. Computational Fluid Dynamics
Optimization of Drift Eliminators: One of the challenges in cooling tower operation is minimizing water loss through drift (water droplets carried by airflow). CFD helps in designing effective drift eliminators by analyzing airflow paths and water droplet behavior, ensuring maximum water retention while minimizing drift.
Design Customization for Specific Applications: Different industries have varying requirements for cooling towers based on their cooling load, water quality, and environmental conditions. CFD allows for customized designs, ensuring that each cooling tower is tailored to the specific needs of the application, whether it’s in HVAC, power generation, or industrial processes.
Reduced Design Time and Costs: Traditionally, physical prototyping was the primary method for testing cooling tower designs, which is expensive and time-consuming. CFD simulations reduce the need for physical prototypes by allowing multiple design iterations to be tested and optimized virtually, leading to faster development cycles and cost savings.
Applications of CFD in Cooling Tower Design
Fan and Airflow Optimization: CFD is critical for optimizing the design and placement of cooling tower fans. It helps ensure optimal air distribution through the fill media, reducing hotspots and improving overall cooling efficiency. By refining fan blade geometry and motor configurations, CFD can also minimize energy consumption and noise levels.
Fill Media Design: The fill media is where heat exchange occurs between water and air. CFD can simulate how water flows through the fill material, helping designers choose the best fill geometry and material for efficient heat transfer. This can lead to significant improvements in the cooling capacity of the tower.
Wind and Environmental Impact: CFD allows cooling tower designs to be tested for environmental factors such as crosswinds, which can disrupt airflow and reduce efficiency. By analyzing how external environmental factors affect the cooling tower, CFD can help mitigate these effects through design adjustments, such as windbreaks or strategic tower placement.
Cooling Tower Placement and Siting: For industrial plants or large facilities that may have multiple cooling towers, CFD can aid in determining the optimal placement of towers to avoid interference or recirculation effects, where exhaust air from one tower is drawn back into another, reducing overall efficiency.
Mitigating Recirculation Effects: Recirculation occurs when the warm, moist air discharged from the cooling tower is drawn back into the tower’s intake. CFD simulations can be used to assess and minimize recirculation, improving the cooling tower’s overall performance and preventing unnecessary energy waste.
Predictive Maintenance and Troubleshooting: CFD can be used to simulate various failure scenarios or degraded performance conditions, allowing operators to anticipate potential issues before they occur. By identifying bottlenecks or areas prone to wear, operators can schedule maintenance more effectively, reducing downtime and operational disruptions.
Environmental Compliance: With stricter environmental regulations surrounding water and air quality, CFD can assist in designing cooling towers that meet these regulations. This includes analyzing plume dispersion and drift patterns to ensure that emissions and water droplets released into the atmosphere do not exceed permissible limits.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Integration with IoT and Sensors: Advances in IoT (Internet of Things) and sensor technology allow for real-time monitoring of cooling tower performance. Combining this data with CFD simulations enables predictive adjustments, improving energy efficiency and extending equipment life.
Sustainable Design Practices: CFD plays a crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of cooling towers. By optimizing water usage, minimizing drift, and reducing energy consumption, CFD-driven designs are helping industries lower their environmental impact and comply with sustainability goals.
Hybrid Cooling Systems: CFD is also being applied to hybrid cooling tower designs, which combine wet and dry cooling technologies to achieve greater efficiency and flexibility in varying climatic conditions. These hybrid systems require precise airflow and heat transfer management, which CFD simulations provide.
Conclusion
Computational Fluid Dynamics has become a game-changer in cooling tower design, offering unmatched precision and flexibility in optimizing performance. From improving thermal efficiency to reducing energy consumption and ensuring regulatory compliance, CFD is driving the future of cooling tower technologies. As industries strive for higher efficiency and sustainability, CFD will continue to play a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of what cooling towers can achieve.